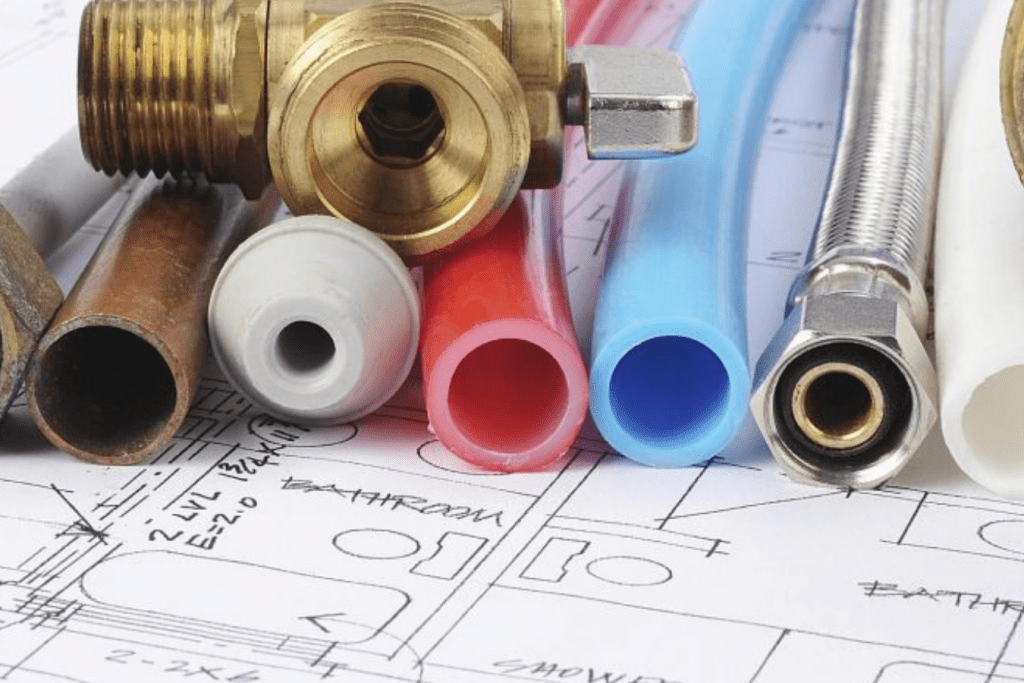
In some cases, due to the different kinds of plumbing pipes available, it can be confusing to work on a DIY plumbing project all by yourself without the experience and knowledge of a qualified plumber. Sometimes the wrong type of pipe will fit but not suit the purpose well and could fail. Choosing the kinds of pipes to be used for drainage system, water supply or sewer can be more challenging compared to the old days when only galvanised steel, or cast-iron pipes were the major pipes used in homes.
In this post, we will be discussing some of the contemporary pipes which can be used in homes as well as their pros and cons.
1. PVC Pipe
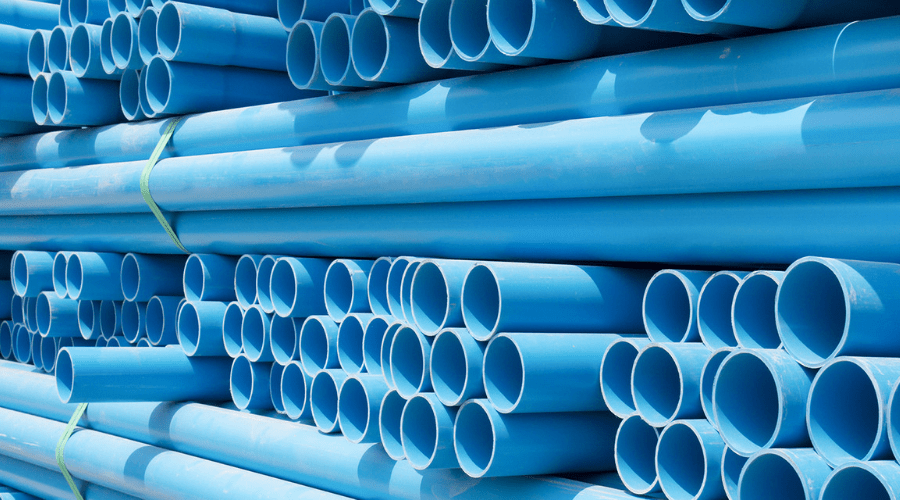

Polyvinyl Chloride (simply known as PVC) pipe is essentially used for drain and vent lines. If you’ve ever unblocked a sink drain you’ll be familiar with its white plastic appearance. At first, PVC was well-known due to its low weight as well as the ease with which it can be used compared to the customary galvanised steel pipe. It can be easily installed, and you will only need a mitre box and hacksaw to cut it. Also, you can easily glue PVC pipes together using a solvent.
Advantages:
- It is flexible.
- It is inexpensive.
- It can be used for a long distance run like irrigation purpose
- Clearly marked diameters are present on the white surface of the pipe.
Disadvantages:
- It is fragile and may shatter
- It is likely to leak when glued.
- It has to be cut rather than unjoin.
2. PEX Pipes
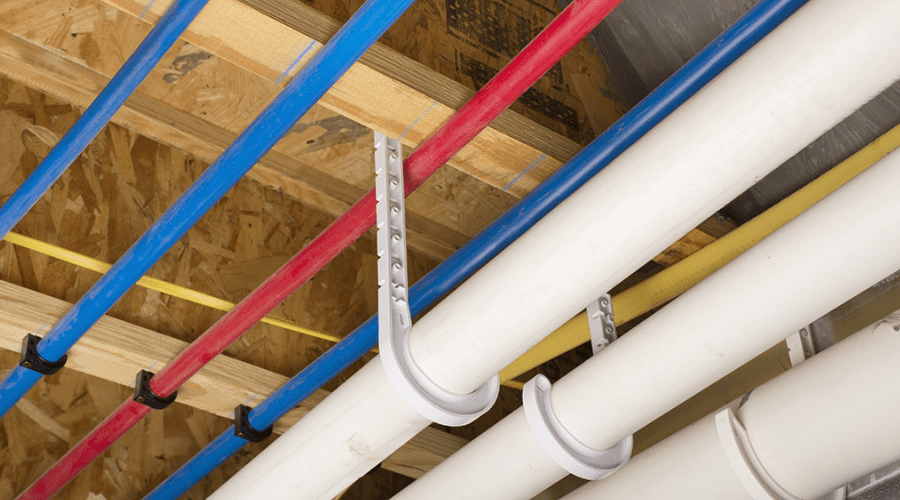

This pipe is also referred to as the cross-linked polyethylene. It is not only a new pipe but one of the most popular pipes in the market. Essentially, cross-linked polyethylene is used to supply water since it is sufficiently strong to tolerate water supply pressure. Also, it is flexible enough to pass through walls, basements, crawlspaces, as well as ceilings. Without a doubt, PEX has been considered as a top-quality water-supply pipe both by professional plumbers and do-it-yourself individuals.
Advantages:
- It can be cut easily
- It is inexpensive
- It can be fixed with push-fit plumbing accessories.
- It is colour-coded; blue for cold water and red for hot water
- It has great flexibility and can curve at angle 90◦.
Disadvantages:
- It is impossible to recycle
- Its long-term effectiveness is not yet verified
- It may leak while attached with push-fit plumbing accessories
3. Rigid Copper Pipe
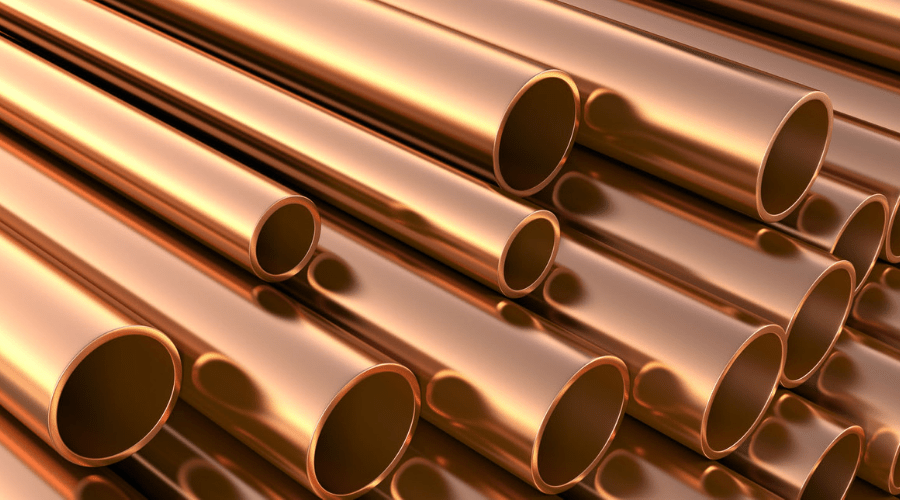

Typically, rigid copper pipe is used as water supply lines in the home. It can be easily cut using a hacksaw or a specific copper tube cutter. Connecting rigid copper pipes is different from others because only a professional can solder the copper pipe. This kind of pipe is an excellent choice for water supply since it does not pose any health risks.
Advantages:
- It can tolerate intense pressure
- It can be recycled easily; water copper pipe can even be sold.
- It can withstand heat considerably.
- It can be bent slightly – even though its name suggests otherwise.
Disadvantages:
- It is costly
- Its internal part may corrode and block water flow over time.
- Since it requires soldering, it can be challenging for the layman to fix.
- It may develop pinhole leaks.
4. ABS Pipe

Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) pipe is suitable for drain and vent lines. ABS and PVC pipes look similar, but the former has a black appearance and softer.
Advantages:
- It is an excellent choice for the underground exterior purpose.
- It is more agile compared to the PVC pipes
- It works effectively in cold temperatures.
Disadvantages:
- It deforms and warps at some specific temperature.
- Most times, it is not allowed by building code.
5. Flexible Copper Pipe
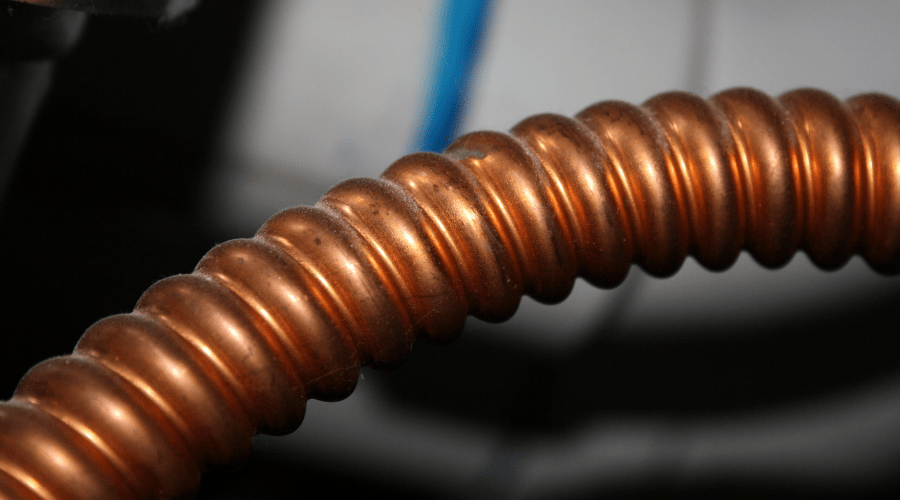
This type of plumbing pipe is applied for the last runs to refrigerators, some certain sinks, and water heaters. Flexible copper pipe is only used for small distance runs, and by using a hacksaw, it can be cut. Also, it can be curved around corners.
Advantages:
- It can tolerate heat significantly.
- It can be applied in tight and uncommon shaped regions.
Disadvantages:
- It is thin and may break.
- It is expensive.
Traditional Plumbing Pipes: Galvanised Steel Pipe and Cast Iron Pipe
Presently, these two traditional kinds of plumbing pipes can only be seen in older homes. They are rarely used most especially by individuals who prefer to do it by themselves.
For several decades, galvanised steel pipes were applied for water supply, drainage, gas supply, and other uses. Even though some people still use galvanised steel pipe for gas supply, it is rarely seen and never applied for water supply in contemporary designs or reconstruction projects. The end of galvanised steel pipes is usually threaded, and each pipe has to be screwed into one another using the point of connections. One particular benefit of the galvanised steel pipe is that it is highly strong. However, this material can corrode and hinder water flow over time. Another drawback of galvanised steel pipe is that it can add lead to the water supply.
Before now, cast iron pipes were mostly used for drainage and sewer applications. However, they can still be seen in some homes currently. Cast iron pipe is effective until it begins to rust completely. It is heavy and stressful to cut. Cast iron pipes have been replaced with rigid plastic pipes by retrofitting like ABS pipes.
I hope this helps understand the different types of pipes in your home and their application. It’s a good idea if you have some storage space in your garage to keep some common pipes and fittings and also make sure you have a basic DIY plumbing toolkit on hand.


